Sitemap
A list of all the posts and pages found on the site. For you robots out there, there is an XML version available for digesting as well.
Pages
Posts
Future Blog Post
Published:
This post will show up by default. To disable scheduling of future posts, edit config.yml and set future: false.
Blog Post number 4
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Blog Post number 3
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Blog Post number 2
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
Blog Post number 1
Published:
This is a sample blog post. Lorem ipsum I can’t remember the rest of lorem ipsum and don’t have an internet connection right now. Testing testing testing this blog post. Blog posts are cool.
portfolio
Tucano: a series of decoder-transformers natively pre-trained in Portuguese
To stimulate the future of open development of neural text generation in Portuguese, we present both GigaVerbo, a concatenation of deduplicated Portuguese text corpora amounting to 200 billion tokens, and Tucano, a series of decoder-transformers natively pre-trained in Portuguese.
Teeny-Tiny Castle: Learning Resources for AI Ethics and Safety
Teeny-Tiny Castle is an open‑source repository that has several examples of how to work ethically and safely with AI.
TeenyTinyLlama: open-source, tiny, and totally Brazilian
TeenyTinyLlama is an open‑source initiative dedicated to developing compact yet capable foundational language models trained natively in Brazilian Portuguese.
Ethical Problem-Solving: a framework to promote the development of safe and ethical artificial intelligence.
Ethical Problem Solving (EPS) is a framework to promote the development of safe and ethical artificial intelligence.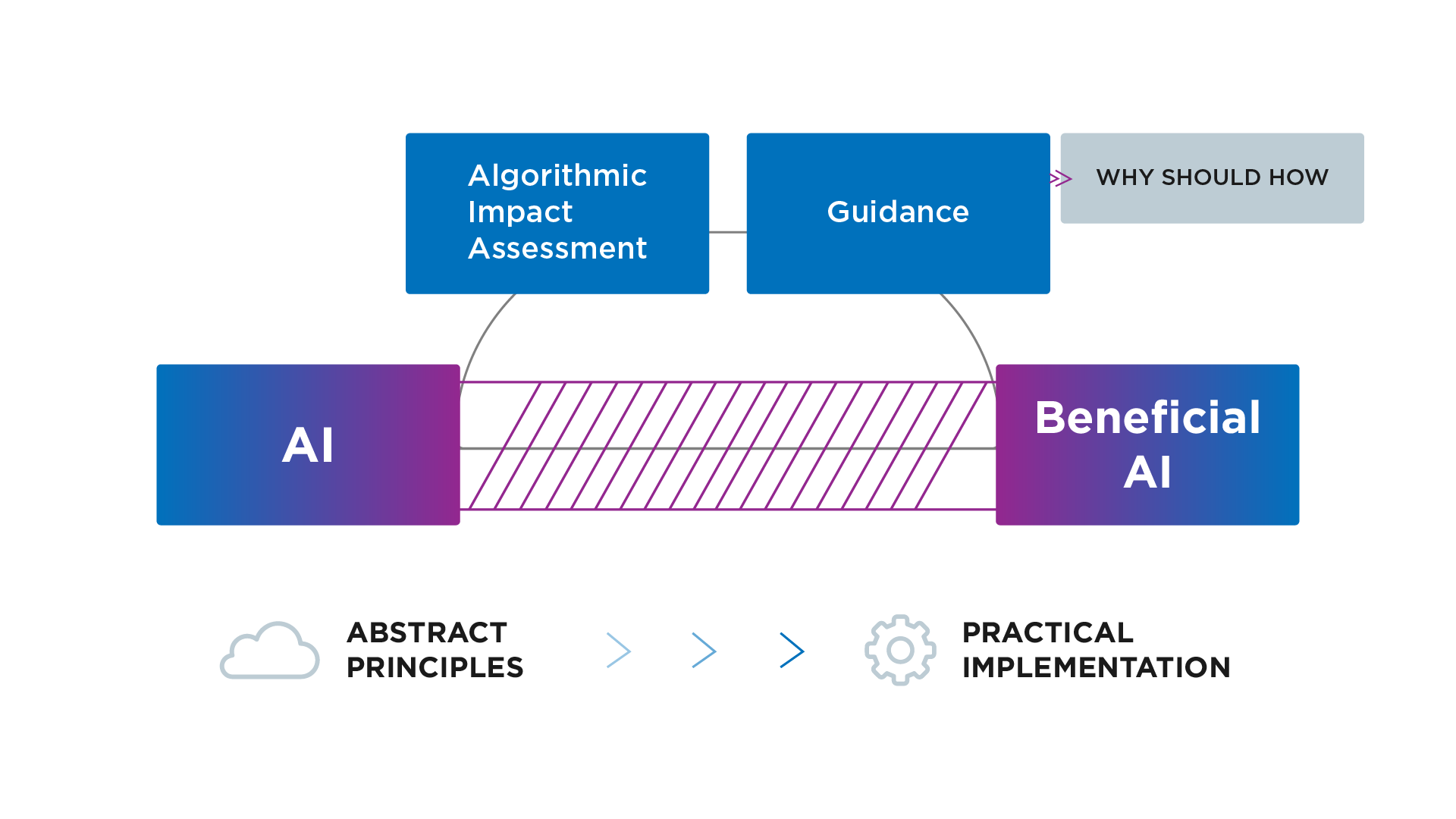
Worldwide AI Ethics: a searchable database for AI Ethics research
The Worldwide AI Ethics (WAIE) dashboard provides an interactive interface for exploring 200 AI governance policies and ethical guidelines collected from governments, industry, academia, and civil society worldwide.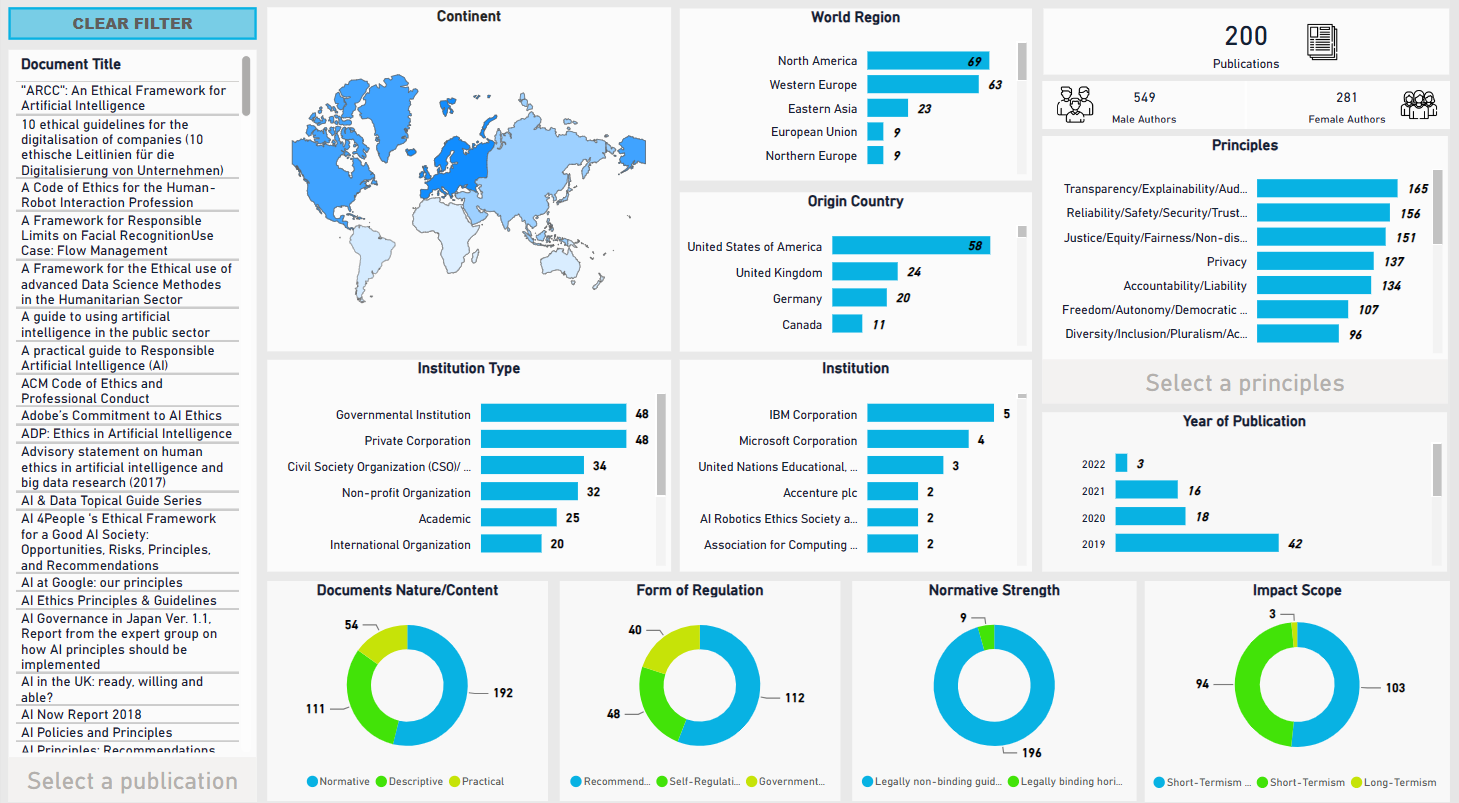
publications
Gender Influence on the Performance of Chest Compressions in Simulated Hypogravity and Microgravity
Published in Aviation, Space and, Environmental Medicine, 2012
In the event of a cardiac arrest during microgravity exposure, external chest compressions (ECCs) which form the main part of basic life support should be carried out while the advanced life support equipment is being deployed. This study was aimed to determine if there was any gender difference in the effectiveness of performing ECCs using a body suspension device to simulate lunar and Martian hypogravity and microgravity.
Muscle Activity during the Performance of CPR in Simulated Microgravity and Hypogravity
Published in American Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 2012
This study compared CPR performance in Earth gravity, hypogravity, and microgravity. While compression rates were consistent, reduced gravity increased heart rate, exertion, and muscle activation, especially in the rectus abdominis and pectoralis major. Findings highlight the need for strong physical conditioning to ensure effective CPR in extraterrestrial environments.
The evaluation of physiological responses during the performance of external chest compressions in simulated hypo and microgravity
Published in Resuscitation, 2012
This study examined CPR performance under Earth gravity, hypogravity, and microgravity. While compression quality remained consistent, rescuers showed higher heart rates, exertion, and altered muscle activation in reduced gravity, indicating greater physical effort is required for effective CPR during space missions.
Development of a skateboarding trick classifier using accelerometry and machine learning
Published in Research on Biomedical Engineering, 2017
This study developed machine learning classifiers for skateboarding tricks using inertial measurement unit data. Artificial neural networks trained on modeled acceleration signals achieved error rates below 0.05%, demonstrating the potential for real-time, accurate trick detection in street skating.
Dynamic Models Applied to Value Learning in Artificial Intelligence
Published in ArXiV, 2020
This paper discusses the challenge of aligning artificial intelligence with human values. It highlights risks of uncritical development, critiques symbolic and connectionist approaches, and proposes dynamic, phenomenological models, such as situated embodied dynamics (SED), as a pathway for safer, value-sensitive AI.
Metanormativity: Solving questions of moral and empirical uncertainty
Published in ethic@-An international Journal for Moral Philosophy, 2020
This study explores metanormativity (norms about norms) as a framework for resolving moral uncertainty. Using vegetarian dilemmas, it applies William MacAskill’s Maximization of Expected Choice-Worthiness, showing how ethical-mathematical models can aggregate conflicting moral theories and guide decision-making under uncertainty.
Singularity and Coordination Problems: Pandemic Lessons from 2020
Published in Journal of Futures Studies, 2021
This paper reviews safety research in AI and examines paradigms that may signal a technological singularity. Using the COVID-19 pandemic as a case study, it highlights humanity’s lack of global coordination in managing existential risks.
Good AI for the Present of Humanity: Democratizing AI Governance
Published in The AI Ethics Journal, 2021
This article connects Cyberpunk and AI Ethics, arguing for a more democratic approach to AI governance. By exposing deficits in current industry power structures, it advocates that public opinion should guide ethical frameworks so “good AI” becomes “good AI for all.”
Technical Note on the Risks of Using Facial Recognition Technologies in Public Security Applications
Published in Whitepaper, 2022
This note examines the expansion of facial recognition in Porto Alegre and outlines the major risks of deploying FRTs for public safety. By integrating technical, legal, and ethical analysis, it clarifies how these systems work, where they fail, and why their use demands careful public scrutiny.
On the Efficiency of Ethics as a Governing Tool for Artificial Intelligence: A Critical Comparison between AI Ethics and Bioethics
Published in ArXiV, 2022
This paper critically examines AI Ethics as a governance tool, arguing that principled guidelines alone are insufficient. It calls for stronger regulation, revised professional training, and integration of bioethics into law to ensure safer, more accountable AI development.
Counterfactual Analysis by Algorithmic Complexity: A metric between possible worlds
Published in Manuscrito, 2022
This study introduces algorithmic complexity as a new method for analyzing counterfactuals. Building on Lewis-Stalnaker’s possible worlds semantics, it offers fresh insights into debates on vagueness, context-dependence, and non-monotonicity, making counterfactual reasoning more intuitive and philosophically robust.
Worldwide AI ethics: A review of 200 guidelines and recommendations for AI governance
Published in Patterns, 2023
This paper analyzes 200 global AI governance policies to identify common ethical principles guiding responsible AI use. By mapping recurring concerns—privacy, discrimination, security, transparency, and other systemic risks—it reveals at least 17 shared principles and evaluates their significance for future regulatory frameworks.
Crossing the principle–practice gap in AI ethics with ethical problem-solving
Published in AI and Ethics, 2024
This work addresses the growing gap between AI ethics principles and their practical implementation. It introduces ethical problem‑solving (EPS), a framework that translates high‑level values into actionable design choices through impact assessments and differential recommendations, offering a concrete path toward responsible, human‑centric AI development.
Dynamic Normativity: Necessary and Sufficient Conditions for Value Alignment
Published in Doctoral Dissertation, 2024
This work reframes AI alignment as a technical‑philosophical problem requiring both solid normative foundations and practical implementation. It introduces Dynamic Normativity, a framework built on necessary and sufficient conditions for value‑aligned learning systems, and demonstrates how these principles can guide the alignment of modern language models.
TeenyTinyLlama: Open-source tiny language models trained in Brazilian Portuguese
Published in Machine Learning with Applications, 2024
This study presents TeenyTinyLlama, a pair of compact, open‑foundation language models designed for Brazilian Portuguese. By addressing the limitations of multilingual LLMs in low‑resource settings, it demonstrates how smaller, permissively licensed models can offer practical, community‑driven alternatives for localized text generation.
Catalog of General Ethical Requirements for AI Certification
Published in Whitepaper, 2024
This whitepaper outlines a practical and normative framework for achieving Trustworthy AI, pairing six core ethical principles with concrete, value‑specific implementation tools. By linking fairness, privacy, safety, sustainability, transparency, explainability, and truthfulness to risk‑assessment criteria aligned with the EU AI Act, it offers stakeholders a blueprint for meeting minimum ethical and certification requirements.
Superalignment With Dynamic Human Values
Published in ICLR 2025 Workshop on Bidirectional Human-AI Alignment (BiAlign), 2025
This work proposes a new alignment framework that unifies scalable oversight with the evolving nature of human values. By training a superhuman reasoning model to decompose tasks and leveraging the part‑to‑complete generalization hypothesis, it outlines a path for ensuring that aligned subtask solutions reliably extend to full, complex behaviors.
Codes of ethics in IT: do they work in isolation?
Published in AI and Ethics, 2025
This study evaluates whether exposure to professional codes of ethics meaningfully shapes ethical decision‑making in IT. Using a randomized controlled trial with a multimedia version of the ACM Code of Ethics, it finds no measurable behavioral impact from passive exposure and argues for exploring more active, engaged forms of ethical intervention in future research.
Technical, legal, and ethical challenges of generative artificial intelligence: an analysis of the governance of training data and copyrights
Published in Discover Artificial Intelligence, 2025
This study analyzes the legal and ethical tensions surrounding generative AI, emphasizing how opaque training data practices undermine copyright compliance and accountability. By comparing regulatory approaches across major jurisdictions, it shows why existing mechanisms remain insufficient and proposes transparency mandates, compensation schemes, and audit tools as a path toward fair and sustainable AI governance.
Tucano: Advancing neural text generation for Portuguese
Published in Patterns, 2025
This study introduces GigaVerbo, a 200‑billion‑token Portuguese corpus, and Tucano, a family of transformer models trained on it. By addressing the resource gap in neural text generation, these models outperform comparable Portuguese and multilingual systems and are released openly to foster reproducible research.
From FLOPs to Footprints: The Resource Cost of Artificial Intelligence
Published in ArXiV, 2025
This study quantifies the material footprint of AI training by linking computational workloads to the elemental composition of modern GPUs. By showing how model scale drives heavy‑metal extraction and hardware turnover, it demonstrates that AI progress carries substantial material costs and argues for integrating resource efficiency into future discussions of AI scalability.
talks
Advancing Neural Text Generation for Portuguese (in English)
Published:
In this talk (in English), I walk through the development of GigaVerbo—the largest Portuguese text dataset at the time of publication—and the Tucano Series, while also situating both within the recent historical evolution of Portuguese‑language LLMs.
IA, ética e soberania em código aberto (in Portuguese)
Published:
In this talk (in Portuguese), I discuss the ethical, political, and technical challenges of building AI in and for Brazil—ranging from value alignment and digital sovereignty to the creation of Tucano and GigaVerbo—while reflecting on the broader landscape of Portuguese‑language AI and the need for more open, locally grounded innovation.
teaching
Teaching experience 1
Undergraduate course, University 1, Department, 2014
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
Teaching experience 2
Workshop, University 1, Department, 2015
This is a description of a teaching experience. You can use markdown like any other post.
